Introduction of TPO, TPV, and TPU Thermoplastic Elastomers

Thermoplastic Elastomers
Introduction of TPO, TPV, and TPU Thermoplastic Elastomers
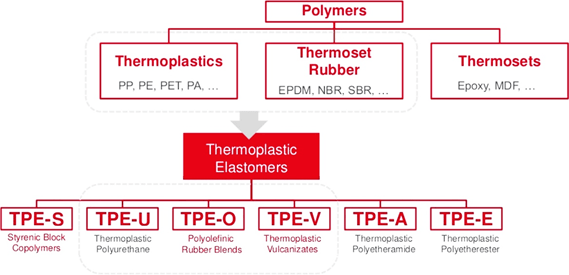
Polymers are divided to four categories: thermoplastics, thermoset rubbers, thermosets and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) which are a group of copolymers or physical combination of plastic and rubber and have both thermoplastic and elastomeric properties (figure1). While the majority of elastomers are thermoset, the most important feature of thermoplastic elastomers is their processing ability. These polymers show both advantages of plastic and rubbers. The benefit of using thermoplastic elastomers is their ability for starching and return to the initial sate, which increase their durability. The main difference between thermoset elastomers and thermoplastic elastomers is the type of crosslinking in their structure. In fact, crosslinking is the key factor which leads to high elasticity properties [1].
1. TPU Types
Thermoplastic elastomers like thermoset rubbers are soft and flexible, and like thermoplastics are processable. In term of structure, they are divided to two main categories: block copolymers, and elastomer compounds. Block copolymers are made by separate crystalline fragments and amorphous regions containing similar polymer chains (Figure 2-a), and blends are mechanical mixtures of semi-crystalline and amorphous polymers (Figure 2-b).
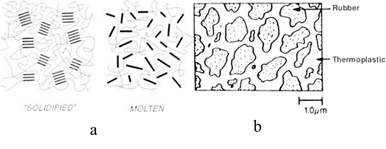
Fig 2. Types of thermoplastic elastomers: a) elastomer compound b) block copolymer
These materials have six commercial types which was at figure1. In this study, three kinds of them will be investigated.
1.1 Polyurethane Thermoplastic (TPU)
This polymer is based on poly ether or poly ester. As it can be seen in figure 3, it has both soft and rigid areas.
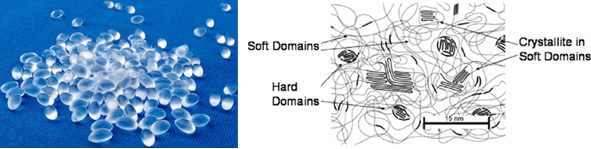
Fig 3. TPU
1.2 Polyolefin-rubber blend (TPO)
In the modified polyolefin elastomers, as it can be seen in figure4, there is a few elastomeric regions in thermoplastic matrix [2].
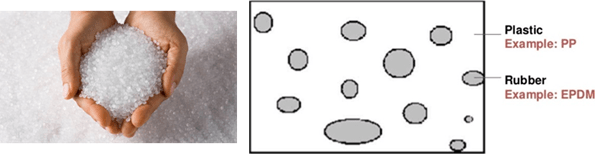
Fig 4. TPO
1.3 Volcanized Thermoplastic (TPV)
The biphasic combination of polypropylene and rubbers, as shown in Figure 5, contains large areas of non-spherical and cross-linked rubbers.
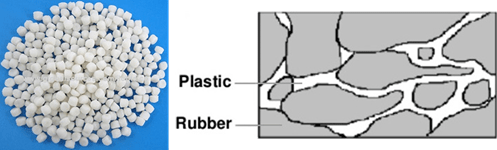
Fig 5. TPV
Each one of commercial thermoplastic elastomers has significant advantages, and due to them for use of them, those benefits should be considered. Applications of thermoplastic elastomers with considering their specific properties are shown in table1.
Table 1. benefits and applications of some commercial thermoplastic elastomers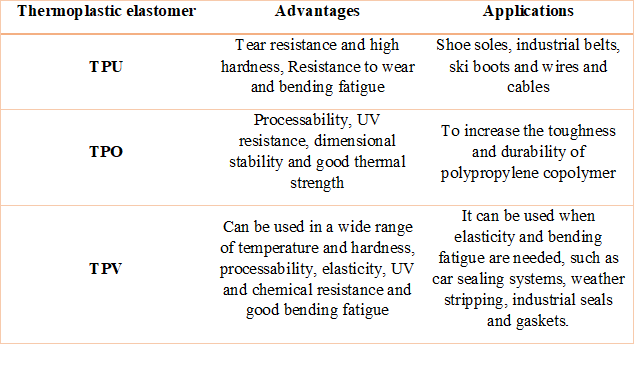
Thermoplastic elastomer Advantages Applications
- TPU Tear resistance and high hardness, Resistance to wear and bending fatigue Shoe soles, industrial belts, ski boots and wires and cables
- TPO Processability, UV resistance, dimensional stability and good thermal strength To increase the toughness and durability of polypropylene copolymer
- TPV Can be used in a wide range of temperature and hardness, processability, elasticity, UV and chemical resistance and good bending fatigue It can be used when elasticity and bending fatigue are needed, such as car sealing systems, weather stripping, industrial seals and gaskets.
2. Properties of thermoplastic elastomers
Elasticity is one of the main properties of TPEs, but there are mix of properties to make them useable in different industries. Whenever it is required to select a TPE, functionality and price of materials must be compared with expected engineering properties. The morphology and chemistry of this polymeric material defines its overall performance. Recent progresses in processing and blending polymers, has expanded the functionality of TPEs. In this section, the most important properties of TPEs are discussed [2].
2.1. Operating temperature and resistance to oils
For the classification of thermoplastic elastomers, their usage/price chart is shown in Figure 6, and as can be seen, the performance range of amorphous and semi-crystalline polymers depends on their price.
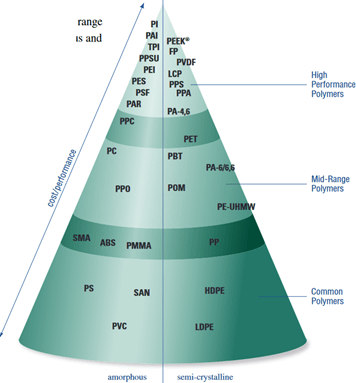
Fig 6. usage/price chart of TPEs
While the cost/performance classification is a general way of classifying thermoplastic elastomers, within this classification, there is considerable variation among its members. Resistance to swelling in hot oil is another criterion that is a suitable classification for the functional properties of these materials. Figure 7 shows the oil resistance of various thermoplastic elastomers compared to their maximum applied temperature [3].
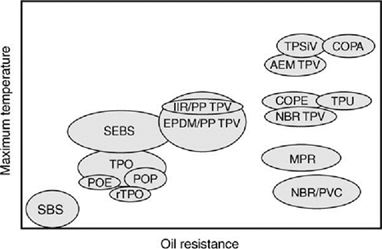
Fig 7. Oil resistance of thermoplastic elastomers
2.2 Hardness
Another major functional comparison between thermoplastic elastomers is their hardness range. Figure 8 shows the hardness range of thermoplastic elastomers. As can be seen, TPUs and TPOs have higher hardness than TPVs.
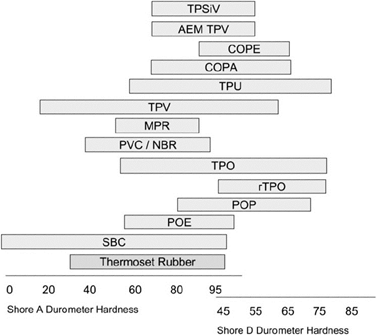
Fig 8. hardness range of thermoplastic elastomers
2.3 Abrasion Resistance
Abrasion resistance is important in performance of thermoplastic elastomers where pulling, rough surface, industrial applications, and contact friction matters. The hard type of these polymer materials usually has better abrasion resistance. TPU and COPA have the highest abrasion resistance.
2.4 Transparency
Most thermoplastic elastomers are opaque. Only some grades are transparent like TPU.
2.5 Tensile and Tear Resistance
Tensile strength and tear resistance are the most important properties in some applications. Typically, hard thermoplastic elastomers have better tear resistance and tensile strength. TPU, COPA and COPE also have the highest tensile and tear resistance.
2.6 permeability Resistance
Resistance to oxygen permeability of most thermoplastic elastomers is almost good. Most of them contain gases such as oxygen and nitrogen for several days or even weeks (depending on local thickness).
2.7 Adhesion and Bonding
When thermoplastic elastomers are bonded onto a substrate or assemble, adhesion and bonding become important functional properties. In general, polar TPEs have very good bendability. For compounds containing polar polymers, polar TPEs are compatible and can create a strong bond. For non-polar substrates such as polypropylene or polyethylene, EPDM/PP TPV, TPOs, IIR/PP TPV and NBR/PP TPV excellent compatibility can be seen.
2.8 Elasticity
An important performance range for TPEs is elasticity. TPVs have a continuous thermoplastic network containing dispersed rubber, their elasticity mechanism is very similar to rubbers.
2.9 Bending Fatigue Resistance
The ability of elastomers to stretch or repeatedly bend, return to its original state and resist crack growth, is bending fatigue resistance. While thermoset rubber compounds are recognized as the best bending fatigue resistant materials, EPDM/PP TPVs have greater bending fatigue resistance.
The following table briefly shows some properties of TPU, TPV and TPO.
Table 2. Some properties of TPU, TPV, and TPO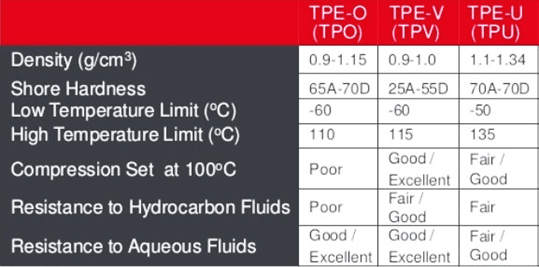
Author: Javad Moftakharian/ Emad Izadi
References
[1] “Thermoplastic elastomer.” [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thermoplastic_elastomer.
[2] “TPE Alphabet Soup: TPO, TPV, SBC, TPU, COPE, COPA.” [Online]. Available: https://www.teknorapex.com/compare-thermoplastic-elastomers-tpe-sbc-tpv-tpo-tpr-rubber.
[3] “TPU.” [Online]. Available: http://www.bpf.co.uk/Plastipedia/Polymers/Thermoplastic_Elastomers.aspx.