Pipe Industry
Pipes are use in various applications, such as water and waste water pipes, floor, wall and ceiling heating systems, hot and warm water systems, and natural gas supply. Plastic pipes are made of polymer materials which have replaced of metal pipes.
The main reasons for the replacing of plastic pipes are properties like high flexibility, low weight, resistance to corrosion and high temperatures, and chemical stability but also their safety and long service life compared to metal pipes.
In most cases, raw polymeric materials show poor properties, which leads to their commercial failure. For example, polypropylene pipes without additives decompose within a few weeks, because they have poor stability against oxidation and heat.
Depending on the nature and chemical properties, additives change the basic properties of the pipe, such as the surface properties, color, performance and durability of the pipe.
In order to create special physical and chemical properties in the pipes, one of the best ways is to use additive masterbatch.
Various masterbatches are used to produce plastic pipes, such as:
- Anti-UV masterbatch:
UV stabilizers protect pipe systems used outdoors for a long time against the damaging effects of UV light.
- Colored masterbatches:
2.1. White masterbatch:
The use of this masterbatch causes the scattering of visible light, and as a result, when it is used in a plastic product, it creates a certain whiteness and brightness.
 Figure 1. White masterbatch in pipes
Figure 1. White masterbatch in pipes
2.2. Black masterbatch:
These additives give pipes a more beautiful appearance, as well as creates a protective layer to increase stability against environmental, chemical, abrasion and impact factors.
- Anti-Oxidant masterbatch:
The pipes are also exposed to oxygen, light, heat, and water flow during their service life. To improve the pipes durability and to protect it against thermo-oxidative degradation during production and service life, the material is stabilized with different types of antioxidants.
4. Processing Aid Masterbatch:
In some cases, in order to prevent melt fracture and fish skin, polymer processing aid are used in the production of pipes.
5. Desiccant Masterbatch:
Some recycle materials, fillers and other additives may have high moisture content due to their polar nature. Therefore desiccant masterbatch is used as a moisture absorber in the pipe production process.
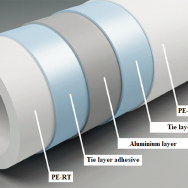
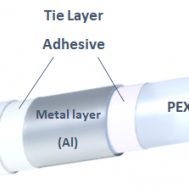
In some cases, tie layer adhesives as a compound use to connect the polyolefin pipes to metals such as aluminum or other components.
- Tie layer adhesive in PEX-Al-PEX and PERT-Al-PERT pipes:
PEX-Al-PEX and PERT-Al-PERT composites are the most widely used types of pipes for radiant floor heating due to their flexibility and durability. These composites consist of two PEX or PERT layers and one aluminum layer between them.
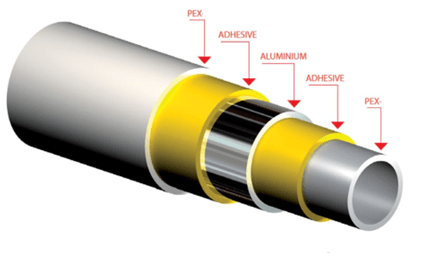 Figure 2. Tie layer adhesive
Figure 2. Tie layer adhesive
- Tie layer adhesive between PE-Steel-PE layers in pipes:
In order to protect metal pipes against corrosion, a polyethylene layer is using on both sides of the metal. Due to low adhesion between polyethylene and metal surface, tie layer adhesive is used.
- Tie layer adhesive between PEX and EVOH layers in pipes:
The problem of low adhesion between EVOH and PEX layers is solved by using tie layer adhesive.
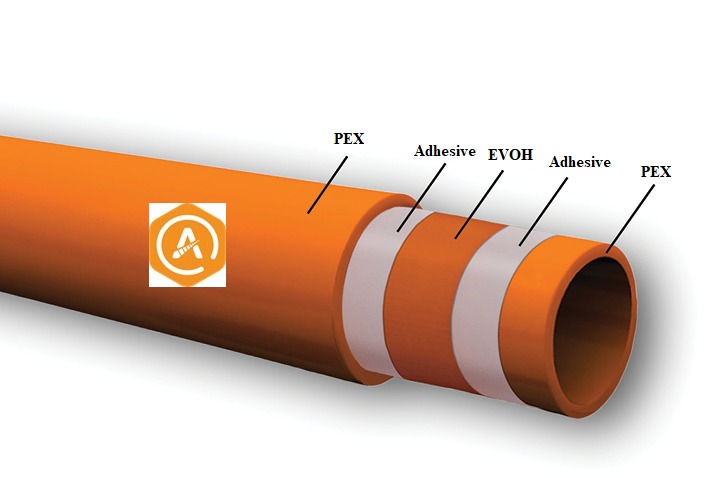 Figure 3. Tie layer adhesive between EVOH and PE
Figure 3. Tie layer adhesive between EVOH and PE
4. Tie layer adhesive between PE and fusion bonded epoxy (FBE) layers in pipes:
In order to prevent separation between polyethylene and metal layers, tie layer adhesives are applied between them.
 Figure 4. Tie layer adhesive between FBE and PE.
Figure 4. Tie layer adhesive between FBE and PE.
Aria Polymer Company is a manufacturer various types of tie layer adhesives that create multi-layer structures with high durability.
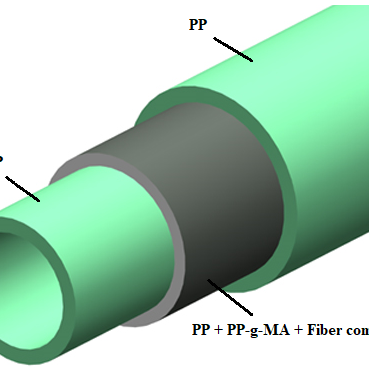
1. Maleated PP:
Maleic PP compatibilizer is used in PP pipes for create compatibility between the fiber composite and PP.